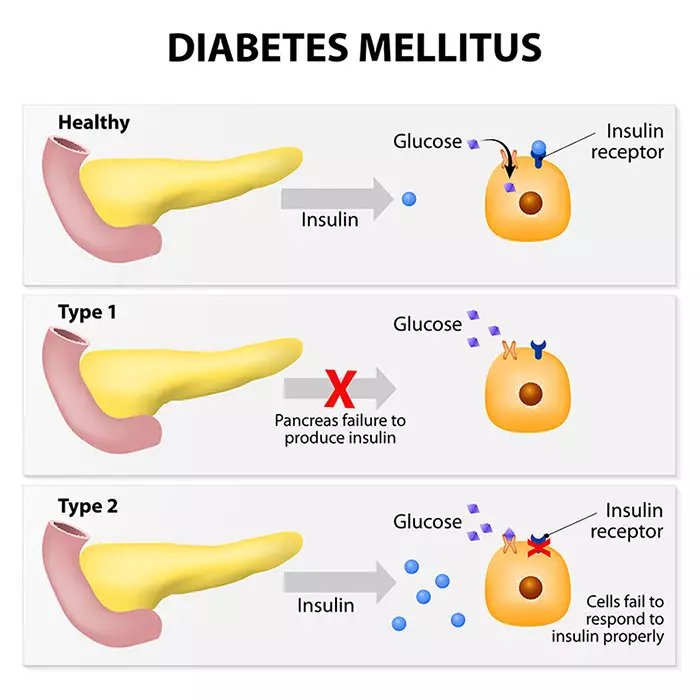
Did you know that approximately 1 in 300 dogs will develop diabetes mellitus during their lifetime? This condition, while serious, is manageable with the right knowledge and care. Diabetes mellitus in dogs is a chronic disease that affects how your dog’s body converts food into energy. It occurs when the pancreas doesn’t produce enough insulin or when the body can’t effectively use the insulin it produces. The purpose of this article is to guide you through the symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and management of diabetes in dogs. Understanding these aspects can make a significant difference in your dog’s quality of life, ensuring they remain happy and healthy companions for years to come.
Causes and Risk Factors
Common Causes of Diabetes in Dogs
Diabetes in dogs often stems from a mix of genetic and environmental factors. One of the primary causes is the inability of the pancreas to produce enough insulin, which is crucial for regulating blood sugar levels. Obesity is another significant contributor, as excess body fat can lead to insulin resistance. Additionally, certain medications and underlying health conditions, like pancreatitis, can also play a role in the development of diabetes.
Risk Factors and Breeds More Prone to the Condition
While any dog can develop diabetes, some breeds are more susceptible. Breeds like Dachshunds, Poodles, and Beagles are often at higher risk. Age is another factor, with middle-aged to older dogs being more commonly affected. Female dogs, especially those that are unspayed, are also at a greater risk. Keeping an eye on these risk factors can help in early detection and management of the condition.
Symptoms and Diagnosis

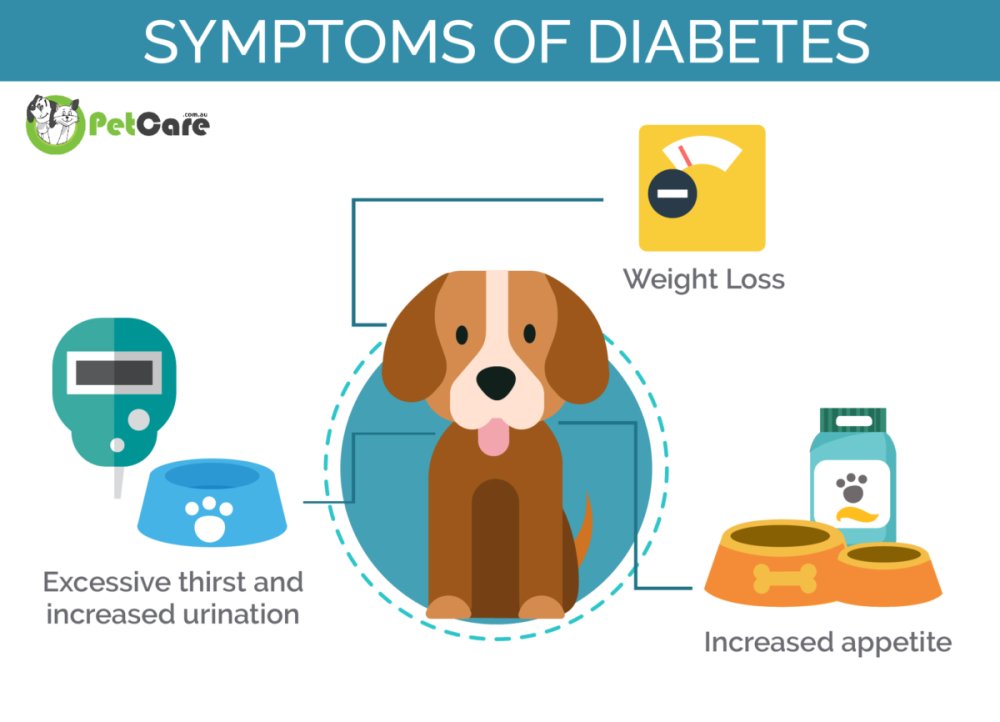
Typical Symptoms of Diabetes in Dogs
Spotting diabetes in dogs early can make a world of difference. Keep an eye out for increased thirst and urination, as these are often the first signs. You might also notice your dog losing weight despite having a good appetite. Lethargy and a dull coat can also be indicators. If your dog seems to be getting more infections, like urinary tract infections, it could be a sign of diabetes. These symptoms can sneak up on you, so it’s important to stay vigilant.
Diagnostic Procedures and Tests Used by Veterinarians
When it comes to diagnosing diabetes, your vet will start with a thorough physical exam and a detailed history of your dog’s health. Blood tests are crucial, as they measure glucose levels and can reveal if your dog is diabetic. A urinalysis is also common, checking for glucose and ketones in the urine. Sometimes, additional tests like a fructosamine test are needed to get a clearer picture of your dog’s condition. Early diagnosis can lead to better management and a healthier life for your furry friend.
Treatment Options

Overview of Insulin Therapy and Its Importance
Insulin therapy is the cornerstone of managing diabetes in dogs. It helps regulate blood sugar levels, which is crucial for your dog’s overall health. Administering insulin might sound daunting, but with practice, it becomes a routine part of your day. The right dosage and timing are key, and your vet will guide you through this process. Consistency is important, as it helps maintain stable glucose levels, reducing the risk of complications.
Dietary Changes and Their Role in Managing Diabetes
Diet plays a big role in managing diabetes. A balanced diet, rich in fibre and low in simple carbohydrates, can help control blood sugar levels. Feeding your dog at regular intervals is also important. This helps prevent spikes in glucose levels. Your vet might recommend a specific diet tailored to your dog’s needs, ensuring they get the right nutrients while managing their condition.
Other Treatment Options and Medications
Besides insulin and diet, there are other medications that might be part of your dog’s treatment plan. Some dogs benefit from oral medications that help improve insulin sensitivity. Regular exercise is also beneficial, as it helps maintain a healthy weight and improves insulin effectiveness. Always consult your vet before making any changes to your dog’s treatment plan, as they can provide the best advice tailored to your dog’s specific needs.
Daily Management and Monitoring
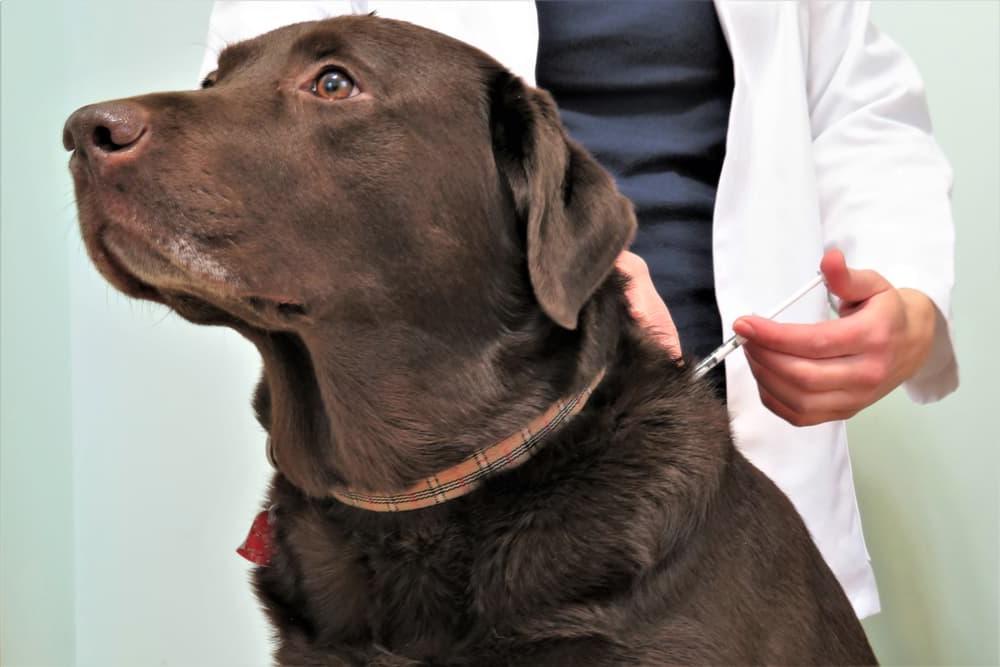
Importance of Regular Blood Glucose Monitoring
Keeping an eye on your dog’s blood glucose levels is crucial. Regular monitoring helps you understand how well their diabetes is being managed. It can alert you to any changes that might need attention, like adjusting insulin doses. This proactive approach can prevent complications and keep your dog feeling their best.
Tips for Managing a Diabetic Dog’s Daily Routine
- Stick to a consistent feeding schedule. This helps regulate blood sugar levels.
- Incorporate regular exercise. It aids in maintaining a healthy weight and improves insulin sensitivity.
- Keep a diary of your dog’s glucose readings, insulin doses, and any changes in behaviour or appetite.
- Ensure your dog has access to fresh water at all times, as dehydration can be a concern.
Signs of Complications and When to Seek Veterinary Help
Be on the lookout for signs like excessive thirst, frequent urination, or sudden weight loss. These could indicate that your dog’s diabetes isn’t well-controlled. If you notice lethargy, vomiting, or a change in appetite, it’s time to call the vet. Early intervention can make a big difference in managing complications effectively.
Diet and Nutrition for Diabetic Dogs
Nutritional Needs for Diabetic Dogs
Managing diabetes in dogs starts with understanding their unique nutritional needs. A diet high in fibre and low in simple carbohydrates is essential. Fibre helps slow down the absorption of glucose, keeping blood sugar levels stable. Protein is also important, supporting muscle maintenance and overall health. Your vet can help tailor a diet plan that meets these needs.
Recommended Foods and Feeding Schedules
Choosing the right food is crucial. Look for high-quality commercial dog foods specifically formulated for diabetic dogs. These often contain the right balance of nutrients. Feeding your dog at the same times each day helps maintain consistent blood sugar levels. Typically, two meals a day, spaced 12 hours apart, works well. Consistency is key.
Foods to Avoid and Portion Control Tips
Steer clear of foods high in sugar and simple carbs, like treats and table scraps. These can cause spikes in blood sugar. Portion control is just as important. Overfeeding can lead to weight gain, complicating diabetes management. Use a measuring cup to ensure accurate portions, and adjust as needed based on your dog’s weight and activity level.
Exercise and Lifestyle
Role of Exercise in Managing Diabetes
Exercise is a game-changer when it comes to managing diabetes in dogs. It helps keep their weight in check and boosts insulin sensitivity, making it easier to control blood sugar levels. Regular activity can also improve your dog’s overall mood and energy levels, which is a win-win for everyone.
Suitable Activities and Exercise Routines for Diabetic Dogs
Not all exercises are created equal, especially for diabetic dogs. Gentle walks, swimming, and even some playtime in the backyard can be great options. The key is consistency. Aim for daily exercise, but keep an eye on your dog’s energy levels and adjust as needed. Short, frequent sessions can be more effective than long, exhausting ones.
Balancing Activity Levels with Insulin and Diet
Finding the right balance between exercise, insulin, and diet is crucial. Too much activity can lower blood sugar levels too quickly, so it’s important to monitor your dog closely. Always coordinate exercise routines with meal and insulin schedules. This ensures your dog gets the most benefit without any risks. Your vet can provide guidance tailored to your dog’s specific needs.
Preventative Care and Long-term Management

Preventative Measures to Reduce the Risk of Complications
Preventing complications in diabetic dogs starts with a proactive approach. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential. This helps catch any fluctuations early, allowing for timely adjustments in treatment. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise is also crucial. Obesity can exacerbate diabetes, so keeping your dog fit is a top priority.
Regular Veterinary Check-ups and Monitoring
Regular vet visits are a must for diabetic dogs. These check-ups allow for ongoing assessment of your dog’s condition and help catch any potential issues before they become serious. Your vet can adjust insulin dosages and dietary plans as needed, ensuring your dog remains in optimal health. Routine blood tests and urinalysis are part of this process, providing a comprehensive view of your dog’s health.
Tips for Maintaining a Good Quality of Life for Diabetic Dogs
- Stick to a consistent daily routine. Dogs thrive on predictability, and this helps manage their condition.
- Provide a balanced diet tailored to their needs. Consult your vet for the best options.
- Ensure regular, moderate exercise to keep them active and healthy.
- Monitor their behaviour and health closely, noting any changes to discuss with your vet.
Final Thoughts
Managing canine diabetes is both challenging and rewarding. With the right knowledge and care, you can significantly enhance your dog’s quality of life. Understanding the symptoms, treatment options, and daily management strategies is crucial in navigating this journey. By staying vigilant and proactive, you can ensure your furry friend remains a happy and healthy companion. Embrace this opportunity to deepen your bond and take action today for a brighter tomorrow.
