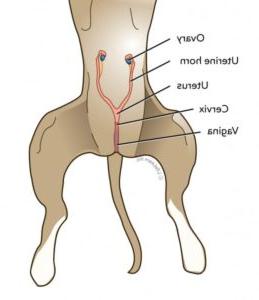
Think all dogs are the same when it comes to reproduction? Not quite. The canine reproductive system is a fascinating and complex network, designed to ensure the continuation of our beloved furry companions. It involves various organs and processes, from the ovaries and testes to the intricate hormonal dance that governs mating and pregnancy. Understanding this system is crucial, especially when it comes to identifying and addressing common reproductive tract issues in dogs. This article aims to shed light on these problems, helping you recognise signs early and seek appropriate care. By being informed, you can ensure your dog leads a healthy and happy life, free from the discomfort and complications that can arise from reproductive health issues.
Common Reproductive Issues in Dogs
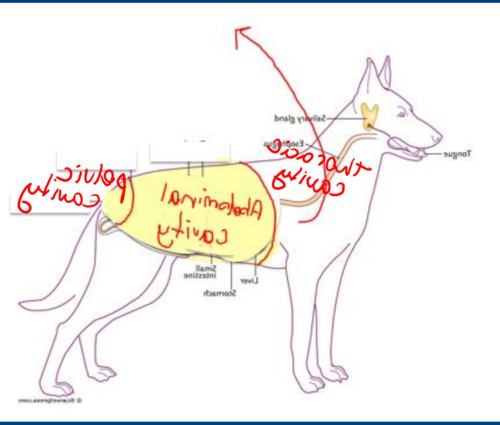
Overview of Typical Reproductive Problems
Reproductive issues in dogs can be quite varied, affecting both males and females in different ways. These problems can range from infections and hormonal imbalances to structural abnormalities. In females, pyometra, a severe uterine infection, is a common concern, especially in unspayed dogs. It can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. Other issues include false pregnancies and irregular heat cycles, which can cause distress and confusion for both the dog and the owner.
Differences Between Male and Female Reproductive Issues
Male dogs, on the other hand, often face problems like testicular tumours or prostate diseases. These conditions can lead to discomfort and may affect their ability to breed. Cryptorchidism, where one or both testicles fail to descend, is another issue that can have long-term health implications. While females might show signs of their reproductive issues through behavioural changes or discharge, males might exhibit discomfort or changes in urination patterns. Understanding these differences is key to ensuring timely and effective treatment.
Female Canine Reproductive Problems
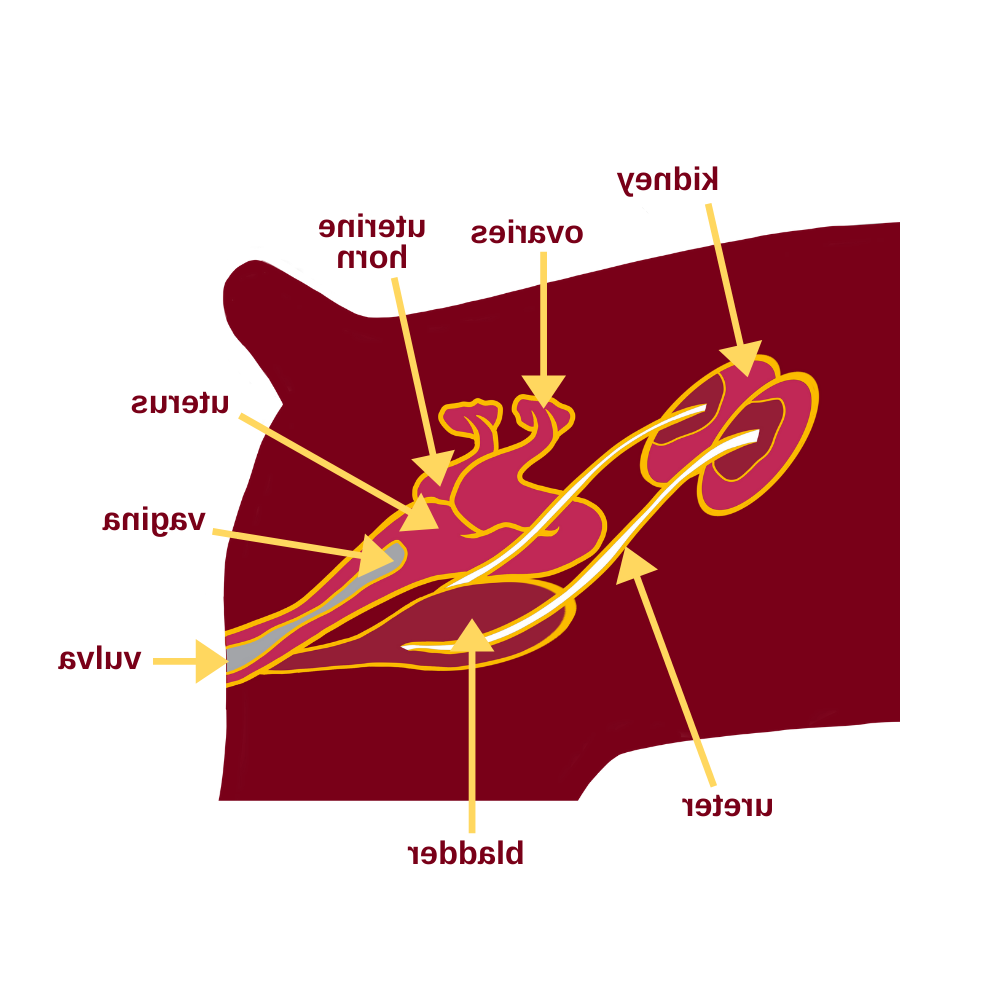
Pyometra: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Pyometra is a serious condition that affects unspayed female dogs. It’s essentially a uterine infection that can become life-threatening if not addressed quickly. The causes are often linked to hormonal changes after a heat cycle, which can lead to bacterial growth in the uterus. Symptoms to watch for include lethargy, loss of appetite, and a pus-like discharge. If you notice these signs, it’s crucial to seek veterinary care immediately. Treatment usually involves surgical removal of the uterus and ovaries, known as spaying, which is the most effective solution.
Ovarian Cysts and Tumours
Ovarian cysts and tumours can also pose significant health risks for female dogs. These growths can disrupt normal hormonal functions, leading to irregular heat cycles or even infertility. While some cysts may resolve on their own, others might require surgical intervention. Regular vet check-ups can help catch these issues early, ensuring your dog stays healthy.
Vaginal Infections and Prolapse
Vaginal infections are another concern, often caused by bacteria or yeast. Symptoms include itching, redness, and unusual discharge. Treatment typically involves antibiotics or antifungal medications. Vaginal prolapse, though less common, is a condition where the vaginal tissue protrudes. It often requires surgical correction to prevent further complications. Keeping an eye on your dog’s behaviour and physical changes can help you catch these issues early.
Male Canine Reproductive Problems
Prostate Disorders: Enlargement, Infections, and Cancer
Prostate issues are quite common in male dogs, especially as they age. An enlarged prostate can cause discomfort and lead to difficulties with urination or defecation. Infections, known as prostatitis, can also occur, often presenting with fever and pain. Prostate cancer, though less common, is a serious concern that requires prompt attention. Regular vet check-ups can help catch these issues early, ensuring your dog stays comfortable and healthy.
Testicular Torsion and Tumours
Testicular torsion is a painful condition where the testicle twists, cutting off its blood supply. This requires immediate veterinary intervention. Testicular tumours are another concern, particularly in older dogs or those with undescended testicles. These tumours can be benign or malignant, and early detection is key to successful treatment. Neutering is often recommended to prevent these issues.
Penile and Preputial Disorders
Penile and preputial disorders can range from infections to injuries. Balanoposthitis, an inflammation of the penis and prepuce, can cause discomfort and discharge. Injuries or foreign bodies can also lead to swelling or pain. Keeping an eye on your dog’s behaviour and any changes in this area can help you catch problems early, ensuring your furry friend stays happy and healthy.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Common Diagnostic Methods
When it comes to diagnosing reproductive issues in dogs, vets have a few tricks up their sleeves. Ultrasound is a go-to tool, offering a clear view of the reproductive organs and helping spot abnormalities like cysts or tumours. Blood tests are also crucial, revealing hormonal imbalances or infections that might be causing trouble. In some cases, X-rays or advanced imaging techniques might be used to get a better picture of what’s going on inside.
Treatment Options for Various Reproductive Issues
Treatment varies depending on the issue at hand. For infections, antibiotics are often the first line of defence. Hormonal imbalances might require medication to regulate cycles or support fertility. Surgical options, like spaying or neutering, are common for conditions like pyometra or testicular tumours. In some cases, less invasive treatments like hormone therapy or lifestyle changes can make a big difference. Regular vet visits and early intervention are key to keeping your dog healthy and happy.
Prevention and Management

Spaying and Neutering Benefits
Spaying and neutering are more than just population control measures. They play a crucial role in preventing serious health issues. For females, spaying eliminates the risk of pyometra and significantly reduces the chance of mammary tumours. Neutering males can prevent testicular cancer and reduce the risk of prostate problems. These procedures can also help curb unwanted behaviours, making life easier for both you and your dog.
Regular Veterinary Check-ups and Screenings
Regular vet visits are essential for catching potential problems early. Routine check-ups can help identify issues like hormonal imbalances or infections before they become serious. Vets can perform screenings and tests to ensure your dog’s reproductive health is in top shape. Early detection often means simpler, more effective treatments, so don’t skip those appointments.
Lifestyle and Dietary Considerations
A balanced diet and active lifestyle are key to maintaining your dog’s overall health, including their reproductive system. Proper nutrition supports hormonal balance and immune function, reducing the risk of infections and other issues. Regular exercise keeps your dog fit and can help prevent obesity-related reproductive problems. Tailoring your dog’s diet and activity level to their specific needs can make a big difference in their long-term health.
Impact on Breeding
How Reproductive Issues Affect Breeding Potential
Reproductive issues can seriously impact a dog’s breeding potential. For females, conditions like pyometra or ovarian cysts can lead to infertility or complications during pregnancy. Males with testicular tumours or prostate disorders might face reduced fertility or even complete sterility. These issues not only affect the dog’s ability to reproduce but can also lead to significant health problems if left untreated. Early detection and treatment are crucial to maintaining breeding potential and overall health.
Ethical Considerations in Breeding Dogs with Reproductive Problems
Breeding dogs with known reproductive issues raises important ethical questions. It’s essential to consider the potential health risks to both the parent dogs and their offspring. Breeding a dog with a genetic predisposition to certain conditions can perpetuate these problems in future generations. Responsible breeders prioritise the health and well-being of their dogs, often opting to remove affected animals from breeding programs. This approach helps ensure healthier, happier dogs and reduces the prevalence of hereditary issues in the breed.
Final Thoughts
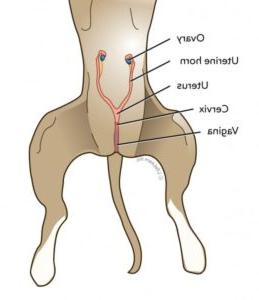
Understanding canine reproductive health is vital for every dog owner. By recognizing the signs of reproductive issues early, you can ensure timely intervention and care. The journey to maintaining your dog’s reproductive health involves balancing preventive measures like spaying and neutering with regular veterinary check-ups. These steps not only safeguard your dog’s well-being but also enhance their quality of life. Stay proactive and informed to support your furry friend’s health and happiness.